Key Uses:
- Organic Synthesis: A fundamental building block for creating diverse organic structures with various functional groups.
- Pharmaceutical Intermediates: Crucial in developing Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) and specialty chemicals.
- Heterocyclic Synthesis: Used to synthesize nitrogen-containing rings (like indoles, pyridines) and other complex ring systems.
- Ester & Amide Synthesis: Serves as a scaffold to form esters and amides through reactions with alcohols and amines, often with high efficiency.
- Knoevenagel Condensation: Accelerates reactions with aldehydes, making it valuable for forming carbon-carbon bonds.
Why it’s Used:
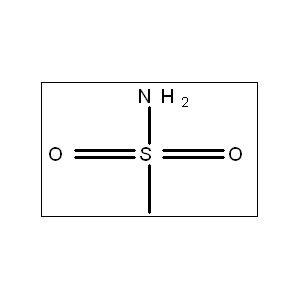
- High Acidity: Its pKa (~4.83) makes it easily deprotonated, forming a stable carbanion.
- Steric Rigidity: Its cyclic structure provides unique reactivity.
- Versatile Reactivity: It’s an excellent starting material for many transformations, acting similarly to malonic esters but with enhanced reactivity, notes Wikipedia and Scimplify.
Applications
Key Uses:
- Organic Synthesis: A fundamental building block for creating diverse organic structures with various functional groups.
- Pharmaceutical Intermediates: Crucial in developing Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) and specialty chemicals.
- Heterocyclic Synthesis: Used to synthesize nitrogen-containing rings (like indoles, pyridines) and other complex ring systems.
- Ester & Amide Synthesis: Serves as a scaffold to form esters and amides through reactions with alcohols and amines, often with high efficiency.
- Knoevenagel Condensation: Accelerates reactions with aldehydes, making it valuable for forming carbon-carbon bonds.
Why it’s Used:
- High Acidity: Its pKa (~4.83) makes it easily deprotonated, forming a stable carbanion.
- Steric Rigidity: Its cyclic structure provides unique reactivity.
- Versatile Reactivity: It’s an excellent starting material for many transformations, acting similarly to malonic esters but with enhanced reactivity, notes Wikipedia and Scimplify.
Applications
- Pharmaceuticals: It serves as a key intermediate in the synthesis of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) and other specialty chemicals for drug development.
- Agrochemicals: It is used as a reagent in the production of various agrochemical compounds.
- Materials Science: The compound is used in the manufacturing of specialty chemicals and polymers.
- Academic Research and Organic Synthesis:
- It is a valuable starting material for synthesizing a wide range of organic compounds, including heterocyclic compounds, beta-keto esters, and carboxylic acids.
- It is used in Knoevenagel condensation reactions, which are C-C bond formation reactions.
- When heated, it produces highly reactive ketenes, which can then be used to form new amides, esters, and rings in a single “one-pot” reaction.
Specific Syntheses
Meldrum’s acid has been used in the synthesis of specific molecules, including:
- Macrocyclic beta-keto lactones
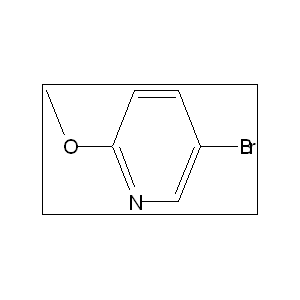
- 4-pyridyl-substituted heterocycles
- 2-substituted indoles
- Isofraxidin
- Pharmaceuticals: It serves as a key intermediate in the synthesis of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) and other specialty chemicals for drug development.
- Agrochemicals: It is used as a reagent in the production of various agrochemical compounds.
- Materials Science: The compound is used in the manufacturing of specialty chemicals and polymers.
- Academic Research and Organic Synthesis:
- It is a valuable starting material for synthesizing a wide range of organic compounds, including heterocyclic compounds, beta-keto esters, and carboxylic acids.
- It is used in Knoevenagel condensation reactions, which are C-C bond formation reactions.
- When heated, it produces highly reactive ketenes, which can then be used to form new amides, esters, and rings in a single “one-pot” reaction.
Specific Syntheses
Meldrum’s acid has been used in the synthesis of specific molecules, including:
- Macrocyclic beta-keto lactones
- 4-pyridyl-substituted heterocycles
- 2-substituted indoles
- Isofraxidin
FAQs