Important Notes:
- Flammability:Highly flammable liquid and vapor, severe fire hazard.
- Reactivity:Reacts with water, moisture, and strong oxidizers.
- Hazards:Causes skin and serious eye irritation; handle with care.
Key Uses
- Organic Synthesis:A crucial intermediate for making complex organic molecules.
- Pharmaceuticals:Used in synthesizing various drugs, including potential anticholinesterase agents.
- Agrochemicals:An intermediate in the production of certain pesticides.
- Phosphorylating Agent:Converts alcohols, amines, and enolates into phosphates.
- Reducing Agent:Reduces nitro compounds to amines and pyridine N-oxide to pyridine.
- Dehydrating Agent:Converts aldoximes into nitriles.
- FragranceIndustry: Used to create unique aroma chemicals by modifying compounds like bindone,
Chemical Role:
- It serves as a building block for phosphorus-containing compounds, often providing the diethyl phosphite group
Key Applications:
- Organic Synthesis: A versatile reagent for introducing phosphorus groups.
- Agrochemicals: Key intermediate for synthesizing organophosphate pesticides, known for anticholinesterase activity.
- Pharmaceuticals: Used as a building block for developing new drugs, especially those targeting anticholinesterase pathways, and in peptide synthesis.
- Fragrance Industry: Can modify compounds like bindone to create novel aroma chemicals.
- Reducing Agent: Can reduce nitro compounds to amines and deoxygenate pyridine N-oxide to pyridine
- Dehydration: Converts aldoximes into nitriles.
FAQs
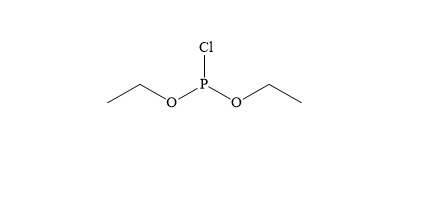
Diethyl Chlorophosphite typically appears as a colorless to pale yellow liquid with a strong, characteristic odor. Pharmaceutical manufacturing Agrochemical production Fine and specialty chemicals Chemical research and development The IUPAC name of Diethyl Chlorophosphite is chloro(diethoxy)phosphine.