Key Uses
- Electrophilic Amination: Introduces amino groups, particularly useful in synthesizing amino acid derivatives and other nitrogen-containing structures, often catalyzed by chiral organocatalysts.
- Asymmetric Synthesis: Key in creating chiral molecules, including:
- Asymmetric Michael additions.
- Asymmetric Friedel-Crafts amination.
- Synthesis of chiral hexapeptide fragments.
- Peptide Synthesis: Used in creating complex peptide fragments and peptidomimetics.
- Mitsunobu Reactions: A reactant for preparing water-soluble prodrugs.
- Heterocycle Synthesis: Precursor for synthesizing dihydropyridazines and pyrroloisoquinolines.
- Dienophile: Reacts with dienes in Diels-Alder type reactions, forming dihydro derivatives.
Chemical Profile & Handling
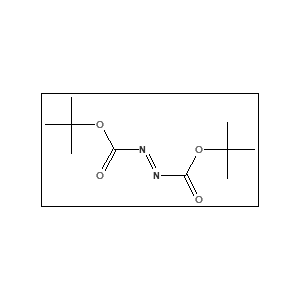
- Synonyms: DBAD, Bis(1,1-dimethylethyl)azodicarboxylate, Di-tert-butyl azodiformate.
- Appearance: Yellow crystalline solid or powder.
- Storage: Sensitive to light and moisture; requires cool (2-8°C) and dark storage, often under an inert gas.
- Safety: Classified as flammable solid (H228) and irritant (H315, H319, H335).
Key Applications:
- Mitsunobu Reactions: Essential for coupling alcohols with acidic nucleophiles, forming new C-N, C-O, and C-S bonds.
- Asymmetric Synthesis: Used in chiral organocatalytic reactions, such as asymmetric Friedel-Crafts amination and Michael additions, to create specific stereoisomers.
- Peptide Synthesis: Key for preparing hexapeptide fragments and dipeptidyl peptidase IV prodrugs.
- Electrophilic Amination: Facilitates the addition of nitrogen to organic molecules, including beta-keto esters, often with chiral catalysts.
- API & Fine Chemical Manufacturing: Serves as a critical building block or catalyst in producing active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and other specialty chemicals.
- Heterocycle Synthesis: Involved in creating complex ring structures like 3,6-dihydropyridazines.
FAQs
Di-Tert-Butyl Azodicarboxylate (870-50-8) is mainly used in Mitsunobu reactions and other organic synthesis applications. The molecular formula of Di-Tert-Butyl Azodicarboxylate (870-50-8) is C₁₀H₁₈N₂O₄.