Introduction
N-Nitroso-N-Methyl Urea (NMU), also known as N-Nitroso-N-methylurea, is a well-known DNA-alkylating agent widely used in cancer research and mutagenesis studies. Identified by CAS Number 684-93-5, NMU has been extensively studied for its ability to induce genetic mutations and tumors in experimental models, making it a critical compound in biomedical and biochemical research.
Due to its potent carcinogenic and mutagenic properties, NMU is strictly restricted to controlled laboratory use and is not intended for commercial, pharmaceutical, or consumer applications.
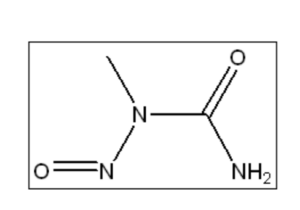 Chemical Identification
Chemical Identification
-
Product Name: N-Nitroso-N-Methyl Urea (NMU)
-
CAS Number: 684-93-5
-
Molecular Formula: C₂H₅N₃O₂
-
Molecular Weight: 103.08 g/mol
Synonyms
NMU is known by several alternative names in scientific literature, including:
-
N-Methyl-N-nitrosourea
-
N-Nitroso-N-methylcarbamide
-
1-Methyl-1-nitrosourea
-
Methylnitrosourea (MNU)
-
Nitrosomethylurea
These synonyms are often used interchangeably in research publications and databases.
Physical & Chemical Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Appearance | Light cream to off-white solid |
| Purity | >95.00% (GC) |
| Melting Point | 119–124 °C |
| Boiling Point | ~193 °C |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO |
| Storage Temperature | 2–8 °C |
NMU is chemically reactive and sensitive to environmental conditions, requiring careful handling and controlled storage.
Mechanism of Action
N-Nitroso-N-Methyl Urea is classified as a direct-acting alkylating agent. Unlike compounds that require metabolic activation, NMU directly transfers methyl groups to DNA bases, particularly at the O⁶-position of guanine.
This alkylation leads to:
-
DNA strand mispairing
-
AT → GC transition mutations
-
Disruption of DNA replication and repair processes
These effects explain its strong mutagenic and carcinogenic potential.
Conclusion
N-Nitroso-N-Methyl Urea (NMU) CAS 684-93-5 is a powerful research chemical with critical importance in cancer biology, mutagenesis, and DNA damage studies. While its hazardous properties limit its use to specialized research environments, NMU continues to play a vital role in advancing scientific understanding of carcinogenesis and genetic mutation mechanisms.
When handled responsibly and within regulatory guidelines, NMU remains an essential compound for advanced biomedical research.

