Uses:
- Pharmaceuticals: Intermediate in creating new drugs, including potential anti-inflammatory and antibacterial agents, and precursors for complex heterocyclic structures like benzodiazepines and quinazolines.
- Agrochemicals: Used in synthesizing pesticides, with research also focusing on its role in breaking down certain pesticides in wastewater.
- Dyes & Materials: Employed in the production of reactive dyes, polyester compounds, and in materials science for developing organic ligands and non-linear optical (NLO) materials.
- Organic Synthesis: A valuable building block for researchers due to its functional groups (nitro and carboxylic acid), allowing for various reactions like reduction, esterification, and amidation to create complex organic molecules.
- Wastewater Treatment: Investigated for its potential as an oxidation catalyst, particularly for degrading pollutants like chlorantraniliprole and reducing chloride levels.
- It’s a nitroaromatic carboxylic acid, combining properties of both acid and nitro groups.
- Its structure allows for diverse chemical transformations, making it a key precursor in advanced synthetic chemistry.
Key Applications:
Pharmaceutical Intermediates: Used in the development of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs), specifically for:
Synthesizing antineoplastic agents like Niraparib.
Creating anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs.
Developing novel Indolin-2-one derivatives that act as protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitors.
Serving as a precursor for sulfonamide antibiotics and kinase inhibitors used in oncology.
Organic Synthesis: Acts as a key intermediate for creating complex heterocyclic systems. It is frequently used to:
- Synthesize 2,3-unsubstituted indolesand quinazoline scaffolds.
-
- Undergo nitro group reduction to produce functionalized aniline derivatives.
- Serve as a building block for esterification and amidation reactions.
- Agrochemicals: Utilized as a building block for the synthesis of herbicides and pesticides.
- Wastewater Treatment: Investigated as an oxidation catalyst effective against pollutants like chlorantraniliprole. It also exhibits photocatalytic activity under visible light when combined with titanium dioxide.
- Dyes and Pigments: Used in the production of azo dyes and other coloring agents for the textile and manufacturing industries.
- Analytical Chemistry: Serves as a standard in chromatographic techniques to measure and analyze compounds in complex mixtures.
- Materials Science: Used to develop organic ligands and nonlinear optical (NLO) materials.
FAQs
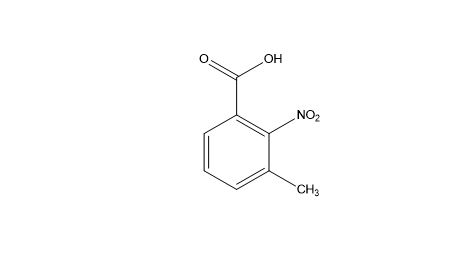
3-Methyl-2-Nitrobenzoic Acid is a substituted nitrobenzoic acid used as a key intermediate in pharmaceutical and fine chemical synthesis. The product is available in high-purity grades suitable for pharmaceutical, laboratory, and industrial applications.