About This Product:
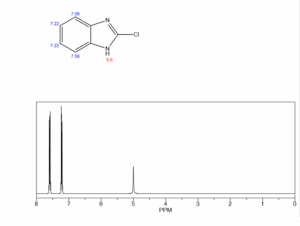
CAS Number : 4857-06-1
Molecular Weight : 152.58
Molecular Formula : C7H5ClN2
Synonym(s) : 2-Chloro-1H-benzo[d]imidazole, 2-CHLORO-1H-BENZOIMIDAZOLE, 2-chloro-1H-1,3-benzodiazole;oro-1H-benzimidazoL, 2-Chlorobenzimidazol;Emestine Impurity 11, 2-CHLOROBENZIMIDAZOLE, 2-Chlorobenzoimidazole
Physical Properties:
Appearance : Off-White to Slight Yellow Powder
Purity : >98.00% (HPLC)
Assay by Titration : > 98%
(On Anhydrous basis)
Melting Point : 205°C – 208°C
Boiling Point : NA
Storage Temperature : Room temperature (recommended dark place)
Conditions to avoid : Moisture sensitive
LOD : NA
Moisture content : NMT 0.50%
Solubility : Soluble in Methanol
Description : It is primarily used in the pharmaceutical and agrochemical industries as a building block for various bioactive compounds like anti-allergy drugs, acid-related medications, and antifungal agents. It is a relatively stable compound that enables efficient synthesis in drug development.
2-Chlorobenzimidazole is primarily used as a versatile intermediate in organic synthesis, especially in the development and manufacture of various pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals.
Key applications include:
- Pharmaceutical Development: It is a crucial building block in the synthesis of many drugs, such as Emedastine and Mizolastine for allergies, and Lansoprazole for acid-related disorders. It is also used in creating anti-malarial, anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, and antiviral agents, including those targeting the hepatitis C virus, and compounds for biochemical studies.
- Agricultural Chemicals: It is used in developing fungicides and herbicides to improve crop protection and productivity.
- Material Science: It can be added to polymers and coatings to increase chemical resistance and durability.
- General Organic Synthesis: Due to its reactivity, it serves as a key starting material for creating other complex organic molecules in laboratories, like 1-methyl-2-chlorobenzimidazole.
2-Chlorobenzimidazole Uses:
2-Chlorobenzimidazole is a versatile intermediate used in industry primarilyh for the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and dyes. It is a key building block in the production of drugs for allergies, acid-related disorders, and inflammation, such as Emedastine, Lansoprazole, and Mizolastine. Its applications also extend to creating antifungal agents, pesticides, and certain pigments.
Pharmaceutical synthesis
- As a building block: It serves as a core structure for building larger, more complex drug molecules.
- For specific drugs: It is used in the synthesis of drugs like Emedastine, Lansoprazole, and Mizolastine to treat conditions such as allergies and acid reflux.
- For anti-malarials: It can be used as a base material for the structural modification and synthesis of benzimidazole anti-malarial drugs.
Agrochemicals
- Fungicides: It is used in the development of antifungal agents for use in agriculture.
- Pesticides: Its antimicrobial and antifungal properties make it useful in the creation of pesticides.
Other chemical applications
- Dyes and pigments: It is used as a component in the formulation of certain dyes and pigments.
- Ligand in coordination chemistry: It can act as a ligand in reactions involving metal coordination.
- Catalyst: It can function as a catalyst in various organic reactions.
Safety and handling
- Hazards: 2-Chlorobenzimidazole is an irritant that can cause skin irritation, serious eye irritation, and respiratory irritation.
- Precautions: When handling, it is important to use appropriate personal protective equipment, such as safety goggles or a face shield, and to ensure adequate ventilation.
- First Aid: In case of contact, follow standard first aid procedures, such as rinsing affected areas with water and seeking medical attention if symptoms persist.
2-Chlorobenzimidazole Reactions:
2-Chlorobenzimidazole undergoes various reactions, primarily as an electrophile, including N-alkylation, which introduces a substituent onto the nitrogen atoms of the ring. It can also undergo ring halogenation, such as bromination, and is a building block for more complex heterocyclic compounds, such as substituted benzimidazole-pyrimidines and various N-substituted 2-chlorobenzimidazole derivatives via nucleophilic aromatic substitution (SNAr).
Key reactions:
- N-Alkylation: Reacts with alkylating agents like dimethyl sulfate, diethyl sulfate, benzyl chloride, or methyl iodide in the presence of a base (e.g., sodium hydride, aqueous NaOH, or KOH) to form N-substituted derivatives.
- Example: Reaction with dimethyl sulfate yields 1-methyl-2-chlorobenzimidazole.
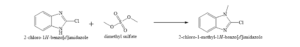
- Halogenation: Can be brominated to form 2-chloro-4,5,6,7-tetrabromobenzimidazole.

- Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution (SNAr): The chlorine atom is susceptible to substitution by nucleophiles, particularly amines, often under high-pressure conditions, to create more complex molecules like astemizole and its analogues.
- Building block: Serves as a starting material for synthesizing other heterocycles, such as 4-amino-6-benzimidazole-pyrimidines

