About This Product:
CAS Number : 3934-20-1
Molecular Weight : 148.98
Molecular Formula : C4H2Cl2N2
Synonym(s) :
- 2-Chloropyrimidin-4-yl chloride;
- 2,6-Dichloro pyrimidine;
- 2,4-Dichloropyrimidine;
- Pazopanib Impurity 45.
Physical Properties:
Appearance : Off-white to light yellow colored solid
Purity : >98.00% (GC)
Melting Point : 57°C – 60°C
Boiling Point : 101°C at 23 mmHg
Storage Temperature : Keep in dark place, sealed in dry, Room temperature
Conditions to avoid : Moisture sensitive
LOD : NA
Solubility : Soluble in Methanol, Chloroform
Description : It is a human skin sensitizer and a versatile organic intermediate used in the synthesis of medicinally important compounds, such as aryl-imidazoles and cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK1) inhibitors, as well as in agricultural and material science applications.
2,4-Dichloropyrimidine Pharmaceutical applications
2,4-Dichloropyrimidine is critical for synthesizing a wide range of biologically active pharmaceutical compounds. These include:
- Antiviral agents: Used in the creation of drugs like HIV reverse transcriptase inhibitors.
- Kinase inhibitors: Key precursor for synthesizing kinase inhibitors used in cancer therapy and other treatments. Examples include Mizolastine, Pazopanib, and Osimertinib mesylate.
- Antibacterial compounds: The pyrimidine scaffold is incorporated to enhance the bioactivity of antibacterial drugs.
- Other drug classes: It is a starting material for compounds with potential anti-inflammatory properties, drugs acting on the central nervous system, and antagonists of corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF1cap C cap R cap F sub 1𝐶𝑅𝐹1) receptors.
Agrochemical applications
In the agrochemical industry, 2,4-dichloropyrimidine is used to produce a variety of crop protection agents, including:
- Herbicides: Used to synthesize agents for controlling unwanted plant growth.
- Fungicides: Incorporated into compounds that protect crops from fungal diseases.
- Insecticides: A precursor for creating insecticides.
Chemical and materials research
The reactive nature of 2,4-dichloropyrimidine makes it a valuable reagent in chemical research and materials science:
- Organic synthesis: It is a standard building block in laboratories for designing new heterocyclic compounds and exploring novel reaction methodologies.
- Coupling reactions: It undergoes highly regioselective double Suzuki coupling reactions to create diarylated pyrimidines.
- Specialty materials: The compound is used in the production of specialty polymers and resins to enhance durability and other material properties.
Other applications
2,4-Dichloropyrimidine also has several other specialized uses:
- Dye and pigment manufacturing: Incorporated into some specialty dyes and optical brighteners to enhance brightness and stability.
- Research reagent: Its use as a standard research reagent helps in biochemical studies related to enzyme inhibition and receptor binding.
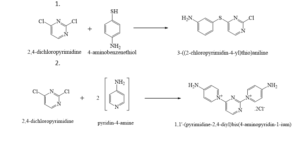
Common uses and reactions
- Pharmaceutical synthesis:Used to create biologically active molecules.
- 4-aryl-5-pyrimidinylimidazoles:Synthesized via sequential Sonogashira coupling and nucleophilic substitution reactions followed by cyclocondensation.
- Cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK1) inhibitors:Used in the synthesis of certain CDK1 inhibitors.
- Suzuki coupling:A one-pot, regioselective double Suzuki coupling reaction can be performed to yield diarylated pyrimidines.
- Nucleophilic aromatic substitution (SNAr):Undergoes regioselective SNAr reactions with amines to produce amino-chloropyrimidines, with the selectivity depending on the reaction conditions and substituents.
- Synthesis of other pyrimidine derivatives:Can be used to make other pyrimidine-based compounds for agrochemicals and specialty organic chemicals.
Some reactions using with 2,4 –Dichloro pyrimidine:
1H NMR Report
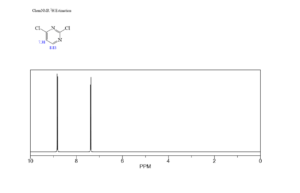 The 1𝐻 NMR spectrum for 2,4-dichloropyrimidine is expected to show two singlet peaks for the two unique protons (H5 and H6), due to the symmetry of the molecule and the lack of adjacent protons to cause splitting. The chemical shift of the protons will be influenced by the electron-withdrawing nature of the chlorine atoms and the nitrogen atoms in the pyrimidine ring, likely appearing in the aromatic region.
The 1𝐻 NMR spectrum for 2,4-dichloropyrimidine is expected to show two singlet peaks for the two unique protons (H5 and H6), due to the symmetry of the molecule and the lack of adjacent protons to cause splitting. The chemical shift of the protons will be influenced by the electron-withdrawing nature of the chlorine atoms and the nitrogen atoms in the pyrimidine ring, likely appearing in the aromatic region.
- H5: This proton is located between the two chlorine atoms and will experience a strong deshielding effect from the adjacent nitrogen and chlorine atoms.
- H6: This proton is adjacent to a nitrogen atom and a carbon atom, which also has a chlorine atom attached.
- Signal splitting: Since there are no protons on adjacent carbons that are not already attached to a chlorine atom, no splitting will occur, and both protons will appear as singlets.
- Chemical shift: Both protons will appear as singlets in the aromatic region, likely with different chemical shifts due to their different chemical environments.