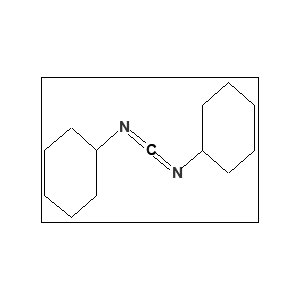
Key Characteristics:
- Moisture Sensitive: Reacts with water and moist air, requiring storage under inert gas.
- Combustible: Stable but combustible.
Key Uses:
A common coupling/dehydrating agent in organic synthesis, particularly for peptides, esters, and amides.
- Peptide Synthesis: Activates carboxylic acids to form peptide bonds, often with additives like HOBt to prevent side reactions.
- Esterification: Helps form esters, even from tertiary alcohols (Steglich Esterification).
- Amide/Nitrile Formation: Dehydrates carboxylic acids with amines to make amides, and with ammonia/amines to make nitriles.
- Oxidation: Used in the Pfitzner-Moffatt oxidation to convert primary/secondary alcohols to aldehydes/ketones.
- Stereochemical Inversion: Inverts the configuration of secondary alcohols.
- Biomedical Applications: Synthesizes copolymers for drug delivery.
How it Works:
DCC reacts with a carboxyl group, forming a highly reactive intermediate that allows efficient coupling with another molecule (like an amine or alcohol). It converts into insoluble dicyclohexylurea (DCU), which is easily filtered out, simplifying purification.
Key Applications:
- Peptide Synthesis: Acts as a carboxyl activator, coupling amino acids to form peptide chains, often with additives like HOBt to prevent side reactions.
- Amide & Ester Formation: Couples carboxylic acids with amines (amides) or alcohols (esters).
- Dehydration Reactions: Converts amides to nitriles and is used in the Moffatt oxidation to turn primary alcohols into aldehydes.
- Biomedical Synthesis: Used in creating copolymers for biomedical uses and in DNA/protein synthesis.
- Stabilizing Agent: Employed as a general stabilizing and condensing agent in organic synthesis.
How it Works:
- DCC removes water (dehydration) to facilitate bond formation, resulting in a byproduct, dicyclohexylurea (DCU), which is easily filtered out.
FAQs The molecular formula of N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC) – 538-75-0 is C₁₃H₂₂N₂.