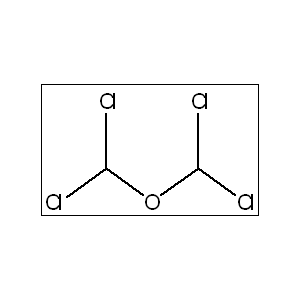
Uses:
Chemical Intermediate: For manufacturing plastics, ion-exchange resins, polymers, paints, and varnishes.
Alkylating Agent: Used to introduce alkyl groups in organic synthesis.
Crosslinking Agent: In the textile industry and resin production.
Chloromethylation: For adding chloromethyl groups to aromatic compounds.
Lab Reagent: Small amounts used in controlled laboratory settings.
Antidote Synthesis: Historically used in making nerve agent antidotes like obidoxime.
Key Considerations:
Extreme Hazard: BCME is a known human carcinogen, leading to strict regulation and limited production.
Formation: Can form spontaneously from formaldehyde and hydrogen chloride, making it a hazardous impurity.
Current Status: Production is minimal and confined to highly controlled, enclosed systems for synthesizing other compounds.
Key Applications
Polymer & Resin Manufacturing: Used to create plastics, ion-exchange resins, and for crosslinking cellulose.
Chemical Synthesis: Acts as an intermediate for organic synthesis, including the preparation of certain nerve agent antidotes (like obidoxime) and for chloromethylation of aromatic compounds.
Textile Industry: Historically used for flame-retardant fabrics and surface treatments for rubber.
Laboratory Reagent: Used in controlled settings for research.
Important Context
Formation: It can form spontaneously from formaldehyde and hydrogen chloride in warm, moist air, and is often a byproduct in the production of chloromethyl methyl ether (CMME).
Safety: BCME is a known carcinogen, so its production and use are extremely limited, occurring only in closed systems with strict safety measures to prevent inhalation exposure.
FAQs Chemical research and reference studies Industrial chemistry (historical use) Regulatory and toxicological analysis Analytical method development