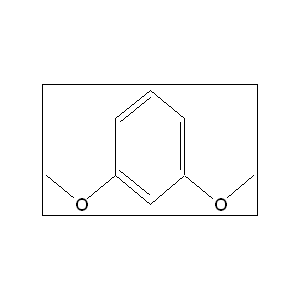
IUPAC Name : 1,3-dimethoxybenzene
Molecular Formula : C8H10O2
Molecular Weight : 138.16 g/mol
Physical Description : Colorless to Pale Yellow Colored Liquid
Boiling Point : 85.00 to 87.00 °C. @ 7.00 mm Hg
Solubility : Miscible With Dichloromethane
Density : 1.053-1.057
Vapor Pressure : 0.52 [mmHg]
CAS No. : 151-10-0
Melting point : -52°C
Purity by GC : NLT 96%
Category : Pharmaceutical intermediate, building blocks
Linear formula : C6H4 (OCH3)2
Synonym(s) : Resorcinol dimethyl ether
Dimethylresorcinol
m-Dimethoxybenzene (meta-Dimethoxybenzene)
3-Methoxyanisole (m-Methoxyanisole)
Benzene, 1,3-dimethoxy- (Chemical Abstracts indexing name)
Benzene, m-dimethoxy-
3-Methoxyphenyl methyl ether